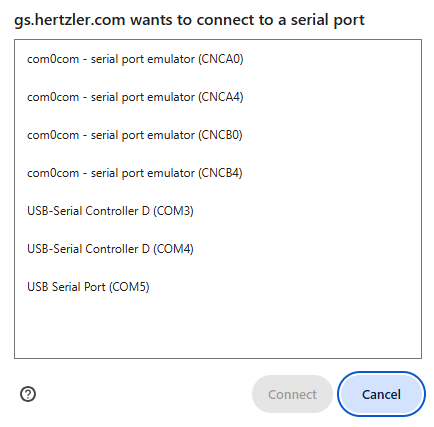
Serial Devices
SPC Tests can be configured to collect readings from connected hardware during an Inspection. Using connected hardware can increase efficiency and reduce manual errors.
This guide explains how to use Serial Devices in Inspections. It assumes that a Serial Device has already been configured in GS, and that the reader is familiar with Inspections and SPC Tests.
Information
Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge are the only browsers that support serial port access. Serial port access is not supported on Android or iOS.
Using SPC Tests
Consider the following Sub-Inspection which collects Length and Width measurements for three 3" bolts. The operator uses a micrometer but must manually type each value into the SPC Tests. This is slow and prone to data entry errors.
Editing the Inspection
The previous Sub-Inspection could be improved by automating data collection using a Serial Device. After setting up the micrometer's Serial Device, you are ready to edit the Inspection:
- Edit the Inspection in the Inspection Designer.
- Select one of the SPC Tests.
- In the right-hand property panel, find the Serial Device property and click Edit.
- Select the micrometer's Serial Device in the resulting overlay.
- Select the other SPC Test and repeat the process.
- Save and Run the Inspection.
Testing the Inspection
When you open the Sub-Inspection, it appears the same as it did before. However, if this is the first time you have run the Inspection, you will be prompted to select the device. This extra security step will appear once for each browser; the browser will remember whether the user has granted permission to a particular device.
Tip
This prompt is filtered by the Serial Device's Vendor ID Filter and Product ID Filter properties.
After granting access to a device, the Sub-Inspection is ready to use:
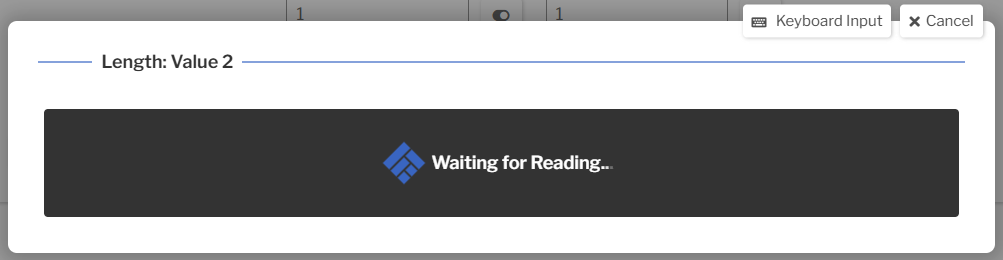
- Click on a value input in the Length SPC Test to bring up the serial overlay.
- Trigger the device, e.g. press the send button on the micrometer.
- Note that the value is automatically inserted into the SPC Test's input.
- GS automatically shifts the focus to the next input of the SPC Test and is ready to receive the next reading.
After an SPC Test is completed, GS automatically focuses on the Width Test, displaying the overlay to receive its readings. After taking these readings, the overlay will close.
Multiple SPC Tests
By default, inputs within a single SPC Test are filled sequentially before moving to the next Test. If an operator prefers to measure all dimensions of a single bolt before moving to the next one, this behavior can be changed:
- Edit the Inspection in the Inspection Designer.
- Click the Settings button for the Sub-Inspection containing the SPC Tests.

- Select Tab To Next SPC Test as the Sub-Inspection's SPC Tab Behavior. Click Confirm.

- Save and Run the Inspection.
- Click on the first input in the Length Test.
The serial overlay will walk through the inputs in order for Length 1, Width 1, Length 2, Width 2, etc. This allows the operator to measure everything on one part before proceeding to the next one.
Using Scripts
There are situations where it is useful to interact directly with a Serial Device through an Inspection Script. This enables:
- Unit conversions, such as converting millimeters to inches.
- Parsing multiple readings from a single message.
- Sending dynamic commands to external devices, such as a multiplexers.
Serial Devices are accessed using gsApi.serial.
Connecting
To connect to a Serial Device saved in GS, use the Device's ID:
Or connect directly if the Device is not saved in GS:
const connection = await gsApi.serial.connect({
baudRate: 9600,
endOfLineString: '\r\n',
splitReadingOn: '|',
valueIndex: 1
});
Reading
The simplest way to retrieve a reading from the connection is to call readNext():
This will wait until the next endOfLineString is received and then return the reading as a string.
If the device requires additional commands to be sent before or after the reading, use the arguments to readNext(). For example, if the device requires R1 to be sent before the reading, and ACK to acknowledge the reading:
Buffering
After the connection is established, all contents sent from the device are stored in the connection's buffer. The buffer is an array of readings delimited by the endOfLineString. If you wish to interact with all these readings, use readAll() and clearBuffer().
Writing
It is sometimes necessary to write additional information to the device in order for it to function correctly. In these situations, use the write() method. For example, if a device must be instructed to start measuring and recording readings using the command START:
Disconnecting
Always disconnect from the device when finished:
Danger
If a script does not call disconnect(), other browser tabs will be unable to access the device (including other tabs running GS). If this occurs, close the tab to release its connection.
Full Code Example
Consider the following situation:
- A mutliplexer is connected to a workstation. This device sends readings simultaneously from a micrometer, a scale, and a torque gauge.
- The individual readings are separated by the
|character. - The multiplexer accepts the
Rcommand to send a set of three individual readings. - The multiplexer sends a newline character (
\n) after each set of three individual readings. - The micrometer reading is reported in millimeters, but the SPC Test expects the value in inches.
- The individual readings are separated by the
- A Sub-Inspection has been created with three SPC Tests and a Button Test. When the Button Test is clicked, the three SPC Tests should be populated.
The following code would satisfy these requirements:
const measurementsSubI = gsApi.inspection.subInspection('measurements');
measurementsSubI.button('read').onClick(async () => {
// Connect to the multiplexer using its hardware settings
const connection = await gsApi.serial.connect({
baudRate: 9600,
endOfLineString: '\n'
});
// Get a reading from the multiplexer using the `R` command.
// This returns 3 readings separated by a pipe
const values = await connection.readNext('R');
const valuesArr = values.split('|');
if (valuesArr.length !== 3) {
return; // Handle the error. An exercise left to the reader.
}
// The first reading is in millimeters, but we need it in inches
const firstReadingInInches = parseFloat(valuesArr[0]) * 0.0394;
// Update the SPC Tests
await measurementsSubI.spc('width').updateProperties({
value: [{ value: firstReadingInInches }]
});
await measurementsSubI.spc('weight').updateProperties({
value: [{ value: parseFloat(valuesArr[1]) }]
});
await measurementsSubI.spc('torque').updateProperties({
value: [{ value: parseFloat(valuesArr[2]) }]
});
});